The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a vital role in workplace safety, including stringent infection control practices tailored for healthcare settings like dental offices. Adhering to OSHA guidelines on procedures such as staff training, PPE usage, hand hygiene, ventilation, and specialized precautions during high-risk procedures is crucial for preventing disease transmission and ensuring patient safety, especially during crises like COVID-19. Implementing and maintaining these infection control procedures are essential for both patients and dental care providers across all services, from preventive dentistry to emergency care.
In today’s healthcare landscape, adhering to robust infection control procedures is paramount for patient safety. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a crucial role in setting standards to mitigate infectious diseases. This article explores essential components of infection control practices that align with OSHA guidelines. We delve into understanding OSHA’s oversight, implementing effective strategies, and maintaining compliance to foster a safer working environment. By following these procedures, healthcare facilities can protect employees and patients alike.
- Understanding OSHA's Role in Infection Control
- Key Components of Effective Infection Control Procedures
- Implementing and Maintaining OSHA-Compliant Practices
Understanding OSHA's Role in Infection Control
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) plays a pivotal role in ensuring workplace safety, including infection control practices. Its standards are designed to safeguard employees from various health hazards, including those associated with infectious diseases. When it comes to healthcare settings, such as dental offices, OSHA provides comprehensive guidelines for infection control procedures. These standards are essential for maintaining a safe environment for both dental professionals and patients, minimizing the risk of disease transmission.
Understanding OSHA’s regulations on infection control is crucial for cosmetic dentistry and preventive dentistry practices. For instance, dental bonding or other restorative procedures should adhere to strict protocols to prevent cross-contamination. By following these guidelines, dental clinics can effectively manage infectious diseases like COVID-19, ensuring a healthy workplace while delivering quality care.
Key Components of Effective Infection Control Procedures
Infection control procedures are an integral part of any healthcare setting, including those focused on oral health like preventive dentistry and tooth repair clinics. These protocols ensure a safe environment for both patients and professionals, minimizing the risk of disease transmission. The key components of effective infection control include comprehensive training for staff, rigorous cleaning and disinfection routines, and standardized protective equipment (PPE) usage. By adhering to these measures, dental practices can create a robust barrier against infections, promoting patient safety and confidence.
Moreover, successful implementation involves staying current with guidelines from organizations like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). This includes regular maintenance of facilities, proper waste management, and efficient air filtration systems. Incorporating innovations such as clear aligners in preventive dentistry further underscores the commitment to infection control procedures, reflecting a proactive approach to patient care that prioritizes both health and aesthetics.
Implementing and Maintaining OSHA-Compliant Practices
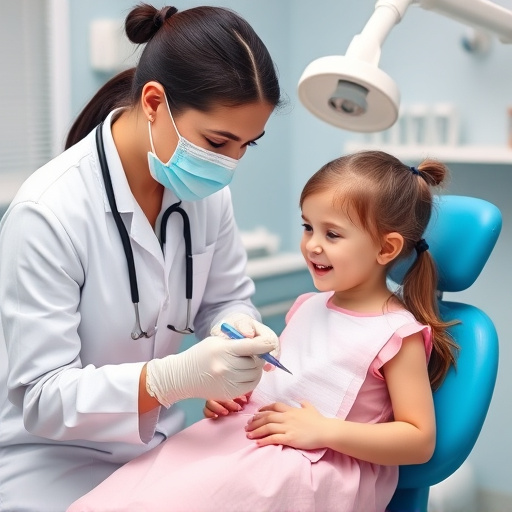

Implementing and maintaining OSHA-compliant infection control procedures is an ongoing process that demands vigilance and adherence to strict standards. These protocols are designed to protect both patients and dental care providers, ensuring a safe environment for everyone involved in dental procedures, including those related to dental implants and emergency dental care. Regular training sessions for staff can help them stay up-to-date with the latest guidelines, fostering a culture of safety.
Effective infection control begins with proper training and continues through consistent application of best practices. This includes using personal protective equipment (PPE), implementing strict hand hygiene protocols, and ensuring adequate ventilation to minimize airborne transmission of pathogens. For procedures like tooth extractions, which carry higher risks due to potential blood exposure, additional precautions must be taken, such as wearing goggles and masks, using sterile instruments, and following up with proper waste disposal techniques to prevent cross-contamination.
Infection control procedures that align with OSHA standards are essential for creating safe work environments, protecting employees, and mitigating risks. By understanding OSHA’s role, implementing key components, and maintaining compliant practices, organizations can effectively prevent the spread of infections and ensure a healthier workplace. These measures not only safeguard employees but also contribute to operational continuity and compliance with legal requirements.