Infection control procedures are essential in family dentistry for patient safety, minimizing cross-contamination risks, and preventing bacterial/viral infections. Strict protocols involve hand hygiene, protective gear, meticulous instrument cleaning (like autoclaving), and disinfection after each patient interaction or procedure (e.g., dental bonding). Adhering to these robust best practices fosters a safe, hygienic environment for both patients and dental professionals, building trust in comprehensive dental care.
In the dental field, ensuring proper infection control procedures is paramount to patient safety and health. This article delves into the essential practices for sterilizing dental instruments, a critical component in minimizing cross-contamination risks. We explore effective sterilization techniques, from autoclaving to chemical disinfection, providing a comprehensive guide for dental professionals. Additionally, we discuss best practices, compliance guidelines, and key considerations to maintain a sterile environment, emphasizing the significance of rigorous infection control procedures in modern dentistry.
- Understanding Infection Control Procedures
- Sterilization Techniques for Dental Instruments
- Best Practices and Compliance Guidelines
Understanding Infection Control Procedures
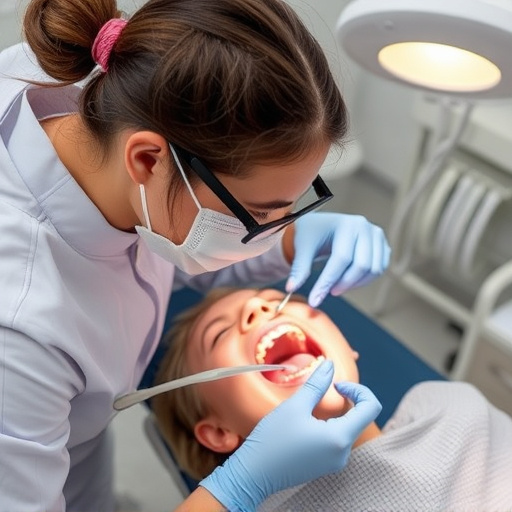
Infection control procedures are essential components of any healthcare setting, but they’re especially critical in family dentistry and comprehensive dental care practices. These protocols ensure that patients receive safe, sterile treatments, minimizing the risk of infections like those caused by bacteria or viruses. Understanding these procedures is paramount for both dentists and their team to maintain a hygienic environment.
Effective infection control involves multiple steps, from proper hand hygiene and wearing protective gear to meticulous cleaning and disinfection of dental instruments after each patient interaction. These measures are crucial not just for tooth repair but also for preventing the transmission of diseases, ensuring patients can trust their dental care experience is both safe and sanitary.
Sterilization Techniques for Dental Instruments
In the realm of family dentistry, maintaining strict infection control procedures is paramount to ensure patient safety and protect dental professionals from hazardous pathogens. Sterilization techniques play a crucial role in this process, eliminating any trace of bacteria, viruses, or fungi from dental instruments used during various procedures, including emergency dental care.
Common sterilization methods include autoclaving, where high-pressure steam kills microorganisms, and chemical disinfection with specific disinfectants effective against a wide range of pathogens. For delicate yet essential procedures like dental bonding, these sterilization techniques are not only recommended but mandatory to prevent cross-contamination. By employing these robust infection control measures, dental professionals contribute to a safe and hygienic environment for both patients and practitioners in the event of emergency dental care.
Best Practices and Compliance Guidelines
Adhering to robust infection control procedures is paramount in dentistry to safeguard patients and dental professionals alike. Best practices involve a multi-layered approach, encompassing proper instrument sterilization using autoclaves or chemical disinfectants, diligent hand hygiene, and donning personal protective equipment (PPE). All staff should be meticulously trained in these protocols and regularly reviewed to ensure compliance with guidelines set forth by regulatory bodies and dental associations.
Compliance is not merely about following rules; it’s a cornerstone of comprehensive dental care. By strictly adhering to infection control procedures, including meticulous cleaning and sterilization techniques for instruments used in tooth repair, dental bonding, or other procedures, we can minimize the risk of cross-contamination and ensure safe, effective treatment for every patient. This commitment not only protects patients’ health but also fosters trust and confidence in the dental care they receive.
Infection control procedures are paramount in ensuring sterile dental practices. By understanding the appropriate sterilization techniques, such as autoclaving and chemical disinfection, along with adhering to best practices and compliance guidelines, dental professionals can significantly minimize the risk of cross-contamination. Effective implementation of these infection control measures not only safeguards patient health but also fosters trust in the dental care provided.